Frequency of notes on a piano - interactive learning object
By Murray Bourne, 31 Jul 2017
Background
An interesting mathematical challenge for musicians throughout the centuries has been the issue of tuning instruments so they sound good when played together. Pythagoras and his followers worked on such problems over 2500 years ago.
For stringed instruments (like violin or cello), this is not such a big concern, because slight changes in finger position can produce a pleasing sound.
But for keyboard players, such flexibility does not exist. They have to hope their piano tuner can get things just right.
There is a catch though. On any piano, only 8 notes (out of the 88 notes on a piano) are actually tuned exactly right. Those are all the A notes, from A-27.5 (which means it has a frequency of 27.5 Hz) up to A-3520 (with frequeny 3,520 Hz).
All the other notes are actually slightly "off" - a compromise so that pianos can sound OK when playing in any key. This is due to the oddities of exponential growth and equal-tempered tuning.
You can read more on the background of this at: What are the frequencies of music notes?
The new applet
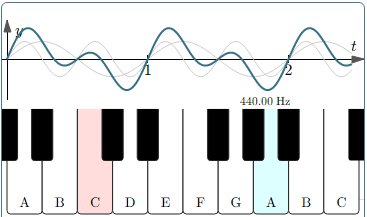
The new applet follows on from the above considerations and allows you to explore the graphs of piano note frequencies. There is a virtual piano that you can play (one note at a time) and after playing each note, you can see the graph of that note and its frequency.
You can find the new applet here:
You can also see a composite signal, which is the sum of the fundamental note A-220 and the note just played.
Here's a screen shot:
Discussion
A-440 and A-220
When you play A-440, the graph looks as follows. They grey one is A-220, and the green one is A-440. You'll notice the frequency of A-440 is twice the frequency of A-220, and the wavelength is half as long. The two curves coincide at each major time point (at 1 and 2 on the t-axis).
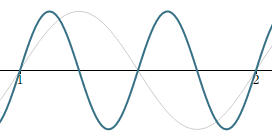
E - the "perfect 5th"
A perfect 5th above A-220 (in theory) is 220× 3/2 = 330 Hz. On a piano, E is actually 329.63 Hz, just a little bit "flat". You can see in the graph there are 1.5 wavelengths for E (the green curve) in the one wavelength of A-220. It's extremely close, and it appears the two curves coincide at t = 1 and t = 2.
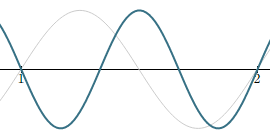
C# - the "major 3rd"
To sound right, a major 3rd "should" have frequency 275 Hz (that is, 5/4 × 220), but is quite "sharp" at 277.18 Hz on a piano.
You can see the green curve is not exactly passing through exactly t = 2. As the frequncies get higher, it becomes increasingly "off".
This was unacceptable to many musicians during the Baroque era, and they would use other tuning methods to make sure the major 3rd sounded better. The downside was they couldn't play in certain other keys at all.
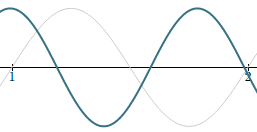
Signal combinations
In the applet, you can also see the combined signal of the fundamental (A-220 in this case), with the note just played.
A-220 and B♭ - 233.08
These two notes are right next to each other on the piano, and sound discordant (bad) when played together. The combined signal gives some insight why. You can see a regular combined signal which is very close to the original two (grey) signals, resulting in "beating" - a kind of shimmering which is not always pleasant. (It can be put to good use in music, but that's for another discussion.)
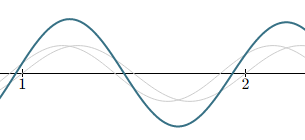
A-220 and C#-275
The major 3rd is one of the most common and "pleasing" sounds in music. On a piano tuned by equal temperament, however, you can see the 3 curves doen't line up so well (the grey A-220, C#-275 and the green combination of the two) because actually, C# is 277.18, which is too sharp for a totally pleasing sound.
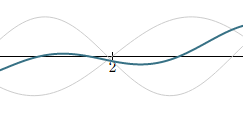
It can't be helped if pianos need to play in any key (which of course, they nearly always need to do).
Conclusion
Piano note frequencies are an interesitng application of trigonometric graphs, exponential growth and music perception.
Once again, here's the link to the applet:
Frequencies of Notes on a Piano: Learning object
See the 4 Comments below.
1 Aug 2017 at 8:39 am [Comment permalink]
This is very nice. Is there any way of making the sound match the combined notes when the composite signal is being displayed? (I don't have a great ear, but so far as I can tell there is no difference in sound between the two settings)
2 Aug 2017 at 5:07 pm [Comment permalink]
Thanks, Alan. I did try to get combined sounds working before publishing. Getting the sounds started was OK, but stopping them both was a different matter!
However, I figured it out and updated the app just now. Please try it again (after a page refresh, if necessary).
6 Feb 2020 at 12:39 pm [Comment permalink]
Hi!, I wanted to ask, how did you manage to combine both graphs.
The graphs of A-220, and C#, look really similar, so I don't understand how they combined together and resulted in the green line.
Please help!!!
Thank you <3
6 Feb 2020 at 3:13 pm [Comment permalink]
@Sofia: The idea with composite graphs is you add the y-values of the 2 (grey) graphs for each point along the x-axis. So if the range of that graph is −1 to 1, on the far left we have about −0.8 + 0.4 = −0.4, which is where the green curve starts on the y-axis. At the first point where the green curve cuts the x-axis, we have approximately −1 + 1 = 0.
You'll see it more clearly how it works for different notes on the page with the app (choose "Combined signal").
This page will help also: Composite Trigonometric Graphs