1. Distance Formula
We use the Distance Forumala to find the distance between any two points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) on a cartesian plane.
See also:
The Cartesian Plane
The cartesian plane was named after Rene Descartes.
See more about Descartes in Functions and Graphs.
Let's start with a right-angled triangle with hypotenuse length c, as shown:
Recall Pythagoras' Theorem, which tells us the length of the longest side (the hypotenuse) of a right triangle:
`c=sqrt(a^2+b^2)`
We use this to find the distance between any two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) on the cartesian (x-y) plane:
The point B (x2, y1) is at the right angle. We can see that:
- The distance between the points A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y1) is simply x2 − x1 and
- The distance between the points C(x2, y2) and B(x2, y1) is simply y2 − y1.
Distance from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2).
Using Pythagoras' Theorem we can develop a formula for the distance d.
Distance Formula
The distance between (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) is given by:
`d=sqrt((x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2`
Note: Don't worry about which point you choose for (x1, y1) (it can be the first or second point given), because the answer works out the same.
Interactive Graph - Distance Formula
You can explore the concept of distance formula in the following interactive graph (it's not a fixed image).
Drag either point A (x1, y1) or point C (x2, y2) to investigate how the distance formula works. As you drag the points the graph will automatically calculate the distance.
Length AB = x2 − x1
Length BC = y2 − y1
Length
Copyright © www.intmath.com
Example 1
Need Graph Paper?
Find the distance between the points (3, −4) and (5, 7).
Answer
Here, x1 = 3 and y1 = −4; x2 = 5 and y2 = 7
So the distance is given by:
`d=sqrt((x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2)`
`=sqrt((5-3)^2+(7-(-4))^2)`
`=sqrt(4+121)`
`=11.18`
Example 2
Find the distance between the points (3, −1) and (−2, 5).
Answer
This time, x1 = 3 and y1 = −1; x2 = −2 and y2 = 5
So the distance is given by:
`d=sqrt((x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2)`
`=sqrt((-2-3)^2+(5-(-1))^2)`
`=sqrt(25+36)`
`=sqrt61`
`=7.8102`
Example 3
What is the distance between (−1, 3) and (−8, −4)?
Answer
In this example, x1 = −1 and y1 = 3; x2 = −8 and y2 = −4
So the distance is given by:
`d=sqrt((x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2)`
`=sqrt((-8-(-1))^2+(-4-3)^2)`
`=sqrt(49+49)`
`=sqrt98`
`=9.899`
Example 4
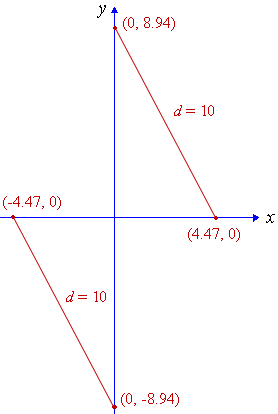
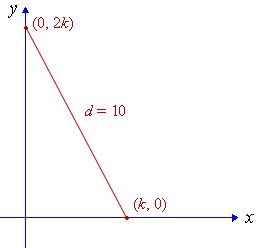
Find k if the distance between (k,0) and (0, 2k) is 10 units.
Answer
This is the situation:
Applying the distance formula, we have:
`d=sqrt((x_2-x_1)^2+(y_2-y_1)^2)`
`=sqrt((2k-0)^2+(0-k)^2)`
`=sqrt(4k^2+k^2)`
`=sqrt(5k^2)`
Now `sqrt(5k^2)=10` so `5k^2=100`, giving:
k2 = 20
so
`k=+-sqrt(20)~~+-4.472`
We obtained 2 solutions, so there are 2 possible outcomes, as follows: