What’s the correct graph of sec(arccos(x))?
By Murray Bourne, 29 Jan 2017
A recent question on the IntMath Forum by Shay asked:
I have the problem sec(arccos 5) and I understand that sec is the reciprocal of cos. But if the domain of arccos is [0,pi] then how can this be 1/5?
This looked interesting and reminded me of a similar issue I wrote abvout before, What is the correct graph of arccot x?.
First, I gently corrected Shay's statement (to point out that the range of arccos is [0,pi], not the domain).
Then I investigated it further with him. Here's some more information.
Some background - inverse cosine
NOTE: The function y = arccos(x) is written in most text books (and on your calculator) as y = cos−1(x). I don't like the latter notation for many reasons (especially because students confuse it with "reciprocal"), so I use the first throughout this article.
Arccos is the inverse cosine function. That is, it works "backwards" compared to the cosine function. You give it a ratio, and it returns an angle (whereas for cosine, you give it an angle, and it returns a ratio).
Examples - cos and inverse cos
cos(60°) = 0.5
arccos(0.5) = 60°
Taking the cos of arccos
Now, since cos and arccos are inverses of each other, it follows that
cos(arccos(x)) = x
and
arccos(cos(x)) = x
But is this always true?
Actually, no.
The graph of y = cos(arccos(x)) starts at (−1,−1) and finishes at (1,1), as you can see below. It's not the "full" graph, y = x, as claimed above.
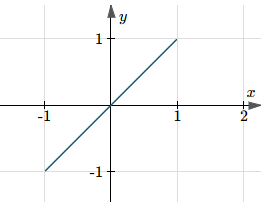
On the other hand, the graph of y = arccos(cos(x)) continues for all x-values, in a saw-tooth pattern involving π, as follows.
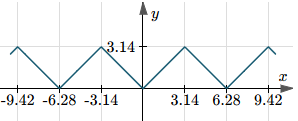
Clearly, neither of the above two graphs is the simple function y = x.
Why is this happening?
The function y = arccos(x) is only defined in the domain −1 ≤ x ≤ 1, (see more in Inverse Trigonometric Functions) so it follows that the cosine of that function, that is
y = cos(arccos(x)),
must also be defined only in that domain.
However, the function y = cos(x) is defined for all x, so when we take the arccos of that function,
y = arccos(cos(x)),
it will be defined for all x as well.
For further background on the domain of a function of a function, see Domain of a Composition (PDF), where it states:
The domain of f ◦ g is the set of all real numbers x in the domain of g such that g(x) is in the domain of f.
Let's return to the original question.
What is the graph of y = sec(arccos(x))?
Since the secant function is defined as:
![]()
then
![]()
We learned above that cos(arccos(x)) is only defined for −1 ≤ x ≤ 1, and it has value x in that domain.
So we have:
![]()
for −1 ≤ x ≤ 1, except x = 0.
Let's now have a look at how some software packages graph it.
Software graphs of y = sec(arccos(x))
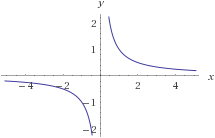
Desmos shows it clearly as having domain −1 ≤ x ≤ 1, except x = 0.
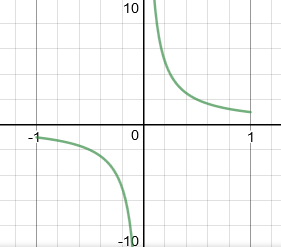
This is the same result as given by JSXGraph:
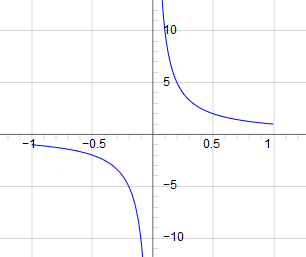
My own Asvg-IM.js also gives the same result.
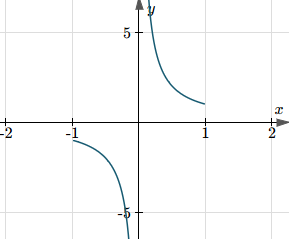
On the other hand, Scientific Notebook gives us the following, with domain all x except x = 0.
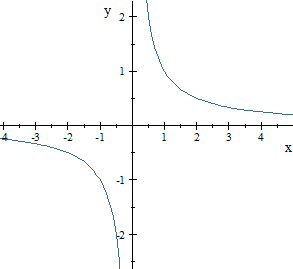
Wolfram|Alpha case
Now, finally, here's how Wolfram|Alpha shows it - with all values of x included, except 0, the same as Scientific Notebook.
So which is the correct graph?
I said in the forum post that I would follow this up with Wolfram|Alpha. I did, and they responded with:
We appreciate your feedback. After review, our internal development group believes the output given is correct:
Domain arcCos gives a complex result whenever x is larger than 1 or smaller than -1, but Sec can still operate on complex numbers to give real values.
For more information please see here.
If you still disagree, please elaborate by providing source links to the specific information that you are interested in seeing.
(That second link was not that helpful.) It wasn't a case of my disagreeing with their result, I was more intent on getting them to make their result more clear.
Arccos x by Wolfram|Alpha
When using the query arccos x (without the "sec"), Wolfram|Alpha first gives the real-valued plot (with domain −1 ≤ x ≤ 1), then goes on to provide the following plot, which has both real parts and imaginary parts shown.
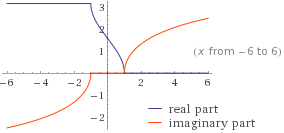
That's good for anyone investigating the function - giving the real case (the one most often needed by undergraduate students of mathematics), then following that with the imaginary case, and stating clearly what is going on.
It was with this in mind that I replied to Wolfram|Alpha with:
Thank you for following up on this - I do appreciate it.
For the W|A result for arccos(x), it clearly separates out the real result and complex result in 2 separate graphs.
I'm wondering if the same approach would make the result for sec(arccos(x)) more understandable. That is, have one graph for the case where x is real (with domain [-1,1], ≠ 0, and another for when x is complex (all x ≠ 0,). Would that still be mathematically sound?
I received a reply:
Thanks for the feedback. I'll pass this on to the developers.
Up to now, there hasn't been any change in the result given for sec(arccos x).
Real properties of sec(arccos x)
Underneath the Wolfram|Alpha graph of sec(arccos x), it states some "Properties as a real function", as follows:
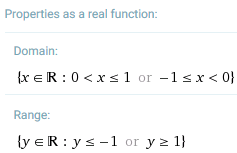
Conclusion
So this is the solution for Shay's question - if we allow for complex values, the domain of sec(arccos x) is "all x except 0" (and the "correct" graph would be the one given by Scientific Notebook and Wolfram|Alpha), but for real values, the function is only defined for −1 ≤ x ≤ 1, except x = 0 (and the "correct" graph would be the one given by the other software packages).
So the answer to his original question is
![]()
assuming 5 is a complex number (which it can be - if the imaginary part happens to be 0), and it is undefined if the function is real.
See the 9 Comments below.
